Alzheimer Rehabilitation: What You Need to Know

Alzheimer Rehabilitation: What You Need to Know
Alzheimer’s rehabilitation aims to improve quality of life, maintain independence, and maximize abilities. Goals include slowing progression, managing symptoms, enhancing communication, promoting mobility, and improving well-being. It takes a personalized and multidisciplinary approach to optimize daily functioning and engagement in meaningful activities.
Approaches to Alzheimer’s Rehabilitation
Cognitive rehabilitation techniques
Key constituents of Alzheimer’s care include cognitive rehabilitation methodologies. These methodologies aim to heighten cognitive performance and enhance one’s capacity to undertake everyday tasks. A technique frequently employed is faultless learning, which guides the individual through tasks with no room for errors, fostering achievement and boosting confidence. Spaced retrieval, another method, is a repetitive practice of recalling information at increasingly longer intervals to boost memory retention. Strategy training is widely used to impart compensating strategies and aid individuals in adjusting to their cognitive difficulties. These methods enable Alzheimer’s patients to retain and fortify their cognitive skills, thereby enhancing their overall living standards.
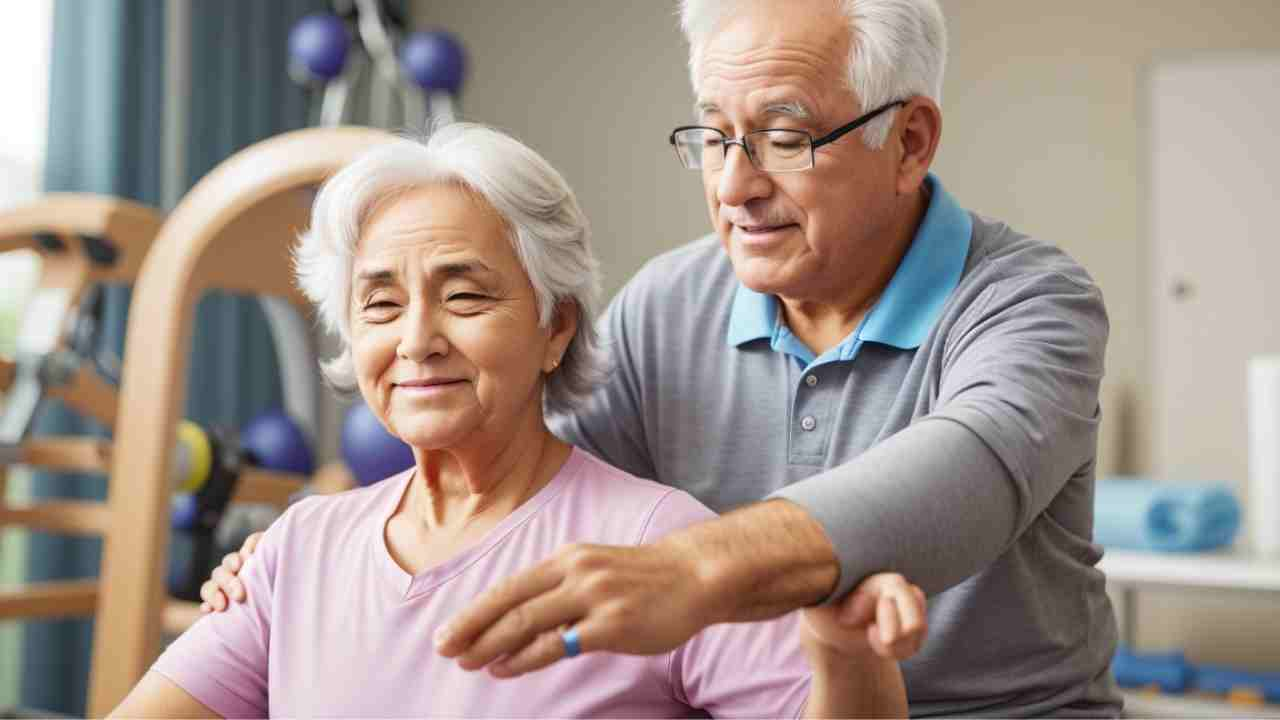
Physical therapy and exercise programs
Essential components of Alzheimer’s care include physical therapy routines and exercise programs. These initiatives focus on enhancing or sustaining the physical abilities of Alzheimer’s patients. Specialized physical therapists develop exercise plans focusing on balance, strength, flexibility, and coordination, reducing fall risks and improving overall mobility. Physical therapy can also provide relief from joint stiffness and muscle tension, thus increasing the patient’s comfort and life quality. The role of exercise programs is to promote cardiovascular health and potentially improve cognitive function. Regular physical activity can decrease the likelihood of developing Alzheimer’s disease by increasing blood flow and stimulating the release of brain-supporting growth factors. Collectively, these physical therapy and exercise programs contribute significantly to the physical well-being and independence of Alzheimer’s patients, boosting their overall rehabilitation process.
Occupational therapy for daily living skills
Occupational therapy is a critical part of Alzheimer’s rehabilitation, focusing on sustaining or enhancing an individual’s capacity for daily living tasks. The therapy intends to address the issues Alzheimer’s patients face in activities such as dressing, bathing, consuming food, and maintaining personal hygiene. Occupational therapists evaluate the patient’s functional competencies and formulate personalized intervention strategies to boost their independence and quality of life. Various techniques and tactics are used, including environmental modification, provision of assistive equipment, and implementation of compensatory strategies to facilitate daily task engagement. Occupational therapists collaborate closely with patients, helping them reclaim or sustain their abilities, adapt to cognitive changes, and foster a feeling of achievement and well-being.
Speech and language therapy for communication
Speech and language care is a valuable component of Alzheimer rehabilitation, aiming to resolve communication challenges faced by Alzheimer’s patients. The therapy focuses on enhancing their spoken, comprehension and expressive abilities. Speech-language pathologists collaborate with Alzheimer’s patients and their families to devise customized treatment plans. Techniques such as reminiscence therapy and reality orientation are used to stimulate language skills and encourage communication. They offer strategies for compensating language-related challenges, like difficulty finding words or understanding deficits. If necessary, robust augmentative and alternative communication aids may be used to foster communication. The goal of speech and language therapy is to boost independence, social engagement, and overall life quality for Alzheimer’s patients.
Strategies for Alzheimer Rehabilitation
Memory enhancement techniques
Memory enhancement techniques play an instrumental role in bolstering and preserving memory functions in persons living with Alzheimer’s. The main goal of these techniques is to activate and fortify the brain’s processes related to memory. Commonly employed techniques often consist of memory aids such as task lists, calendars, and reminder applications intended to assist individuals in remembering significant events and activities. Moreover, mnemonic tools such as visual imagery, acronyms, and associations aid in bolstering memory recall. It’s crucial to note that practice and repetition are the pillars of memory enhancement techniques, as continuous participation in memory exercises can reinforce neural connections, leading to improved memory preservation. Furthermore, engaging in mentally stimulating tasks like puzzles, reading, or acquiring new skills can foster brain activity and boost memory functions. Personalization of these memory enhancement techniques based on the individual’s needs and abilities is essential, along with collaborating with healthcare experts in Alzheimer’s rehabilitation to devise an effective plan to enhance memory.

Behavior management strategies
Behavior management strategies are instrumental in Alzheimer’s rehabilitation as they address behavioral challenges and symptoms associated with Alzheimer’s. The aim of these strategies is to foster a secure and nurturing environment for people with Alzheimer’s, helping in reducing distress and restlessness. A strategy that is particularly effective is the establishment of routine and structure which provides predictability and minimizes confusion**. Employing direct, uncomplicated instructions and molding the environment to encourage calmness and relaxation**, for instance, through various techniques such as music therapy and aromatherapy, is also beneficial. An open line of communication with the individual, along with their involvement in decision-making, further enhances behavior management. Personalizing these strategies according to the unique needs of every individual, taking into account their personal preferences and triggers, is crucial. With appropriate behavior management strategies, people living with Alzheimer’s can witness improved overall well-being and quality of life.
Sensory stimulation interventions
In Alzheimer’s rehabilitation, sensory stimulation interventions are at the core of treatment. The aim is to engage and stimulate the senses, including sight, hearing, touch, taste, and smell, thereby enhancing cognitive and emotional functions. Commonly used techniques in sensory stimulation include sensory rooms, music therapy, aromatherapy, and multisensory activities**. Sensory rooms are spaces designed to deliver diverse sensory experiences through lights, sounds, textures, and objects**. Aromatherapy harnesses essential oils to stimulate the sense of smell and induce relaxation, while music therapy uses music to elicit emotional responses and ameliorate mood, memory, and communication. Engaging multiple senses at the same time through multisensory activities such as textured painting or taste testing different flavors also proves helpful. Overall, these interventions help to manage agitation, uplift mood, induce relaxation, and generally improve the wellbeing of individuals living with Alzheimer’s.
Supportive Care and Resources
Instructional programs and resources for caregivers are crucial for those tending to individuals afflicted with Alzheimer’s disease. These crucial initiatives arm caregivers with the requisite knowledge and capability to assist their loved ones aptly, comprehend the disease’s progression, handle difficult behaviors, and uphold a secure and mentally engaging surrounding. Caregiver instructional endeavors typically encompass training sessions, workshops, and communal support platforms that provide insights on diverse facets of Alzheimer’s care such as managing medication, implementing communication strategies, and stress-handling techniques. These instructional initiatives can significantly transform the caregivers’ experiences by alleviating their stress, bolstering their skill to meet the exhaustive demands of caregiving, and augmenting the standard of care delivered to Alzheimer’s patients.
Bibliography
- Perra, A., Riccardo, C. L., De Lorenzo, V., De Marco, E., Di Natale, L., Kurotschka, P. K., … & Carta, M. G. (2023). Fully immersive virtual reality-based cognitive remediation for adults with psychosocial disabilities: a systematic scoping review of methods intervention gaps and meta-analysis of published effectiveness studies. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(2), 1527. (https://www.mdpi.com/1660-4601/20/2/1527)
- De la Rosa, A., Olaso-Gonzalez, G., Arc-Chagnaud, C., Millan, F., Salvador-Pascual, A., García-Lucerga, C., … & Gomez-Cabrera, M. C. (2020). Physical exercise in the prevention and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of sport and health science, 9(5), 394-404. (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2095254620300119)
- López-Ortiz, S., Pinto-Fraga, J., Valenzuela, P. L., Martín-Hernández, J., Seisdedos, M. M., García-López, O., … & Santos-Lozano, A. (2021). Physical exercise and Alzheimer’s disease: effects on pathophysiological molecular pathways of the disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(6), 2897. (https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/22/6/2897/pdf)
- Ham, M. J., Kim, S., Jo, Y. J., Park, C., Nam, Y., Yoo, D. H., & Moon, M. (2021). The effect of a multimodal occupational therapy program with cognition-oriented approach on cognitive function and activities of daily living in patients with Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Biomedicines, 9(12), 1951. (https://www.mdpi.com/2227-9059/9/12/1951)
- Lanzi, A. M., Saylor, A. K., & Cohen, M. L. (2022). Survey results of speech-language pathologists working with cognitive-communication disorders: Improving practices for mild cognitive impairment and early-stage dementia from Alzheimer’s disease. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 31(4), 1653-1671. (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9531927/)
- Matziorinis, A. M., & Koelsch, S. (2022). The promise of music therapy for Alzheimer’s disease: A review. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1516(1), 11-17. (https://nyaspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdfdirect/10.1111/nyas.14864)
- Anderson, M. S., Homdee, N., Bankole, A., Alam, R., Mitchell, B., Hayes, J., … & Lach, J. (2020). Behavioral interventions for Alzheimer’s management using technology: home-based monitoring. Current Geriatrics Reports, 9, 90-100. (https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s13670-020-00312-y)
- Yang, H., Luo, Y., Hu, Q., Tian, X., & Wen, H. (2021). Benefits in Alzheimer’s disease of sensory and multisensory stimulation. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 82(2), 463-484. (https://content.iospress.com/articles/journal-of-alzheimers-disease/jad201554)